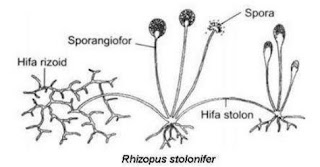
Zygomycetes include mushroom bread, Rhizopus stolonifer, which rapidly propagates on the surface of bread, fruits, and vegetables. They are mostly terrestrial in their habitats, living on the ground or in plants and animals.
Most species of saprophyte mean they live from decomposing organic matter. Some are parasites in plants, insects, and small animals, while others form a symbiotic relationship with plants.
Zygomycetes play a considerable commercial role. Another species Rhizopus metabolic product is an intermediate in the synthesis of semi-synthetic steroid hormones.
The characteristics of Zygomycota
Zygomycota has the following characteristics:- The hyphae are not insulated and coenocytic (has several cores).
- Cell walls are composed of chitin.
- Asexual and sexual reproduction.
- Hyphae serve to absorb food, called rhizoid. Example: Rhizopus stoloniferous.
Zygomycota has a coenocytic hifa talus in which the nucleus is haploid when the organism is in a vegetative stage. Fungi usually reproduce asexually by producing sporangiospores. Black tips mushroom bread, Rhizopus stolonifer, is a swollen sporangium packed with black spores. When the spores attach to a suitable substrate, they germinate and produce a new mycelium.
Sexual reproduction begins when conditions become unfavorable. Two opposing mating strains (type + and type -) must be near to gametangia (single: gametangium) of hyphae to be produced and fused, leading to karyogamy.
Developed diploid zygospores have thick coats that protect them from drying and other hazards. They may remain dormant until the environmental conditions become good.
When the zygospore germinates, it undergoes meiosis and produces haploid spores, which will, in turn, grow into new organisms. The form of sexual reproduction in the fungus is called a conjugate (though distinctly different from the conjugation in bacteria and protists), giving rise to the name "conjugated fungus".
Summary
- Most Zygomycota is saprophytes, while some are species of parasites.
- Usually, Zygomycota reproduces asexually by producing sporangiospores.
- Zygomycota reproduces sexually when environmental conditions become unfavorable.
- To reproduce sexually, two opposing mating strains must be fusing or conjugated, thus, sharing the genetic content and creating zygospores.
- The resulting diploid zygospores remain active and protected by a thick coat until environmental conditions have improved.
- When the condition becomes good, zygospore undergoes meiosis producing haploid spores, which will eventually grow into new organisms.
- Karyogamy is a fusion of two nuclei in the cell.
- Conjugation is a temporary fusion of organisms, especially as part of sexual reproduction.
- Zygospores are spores formed by a combination of several zoospores.
- Zygomycetes is an organism of the phylum Zygomycota.